

Employee stock ownership plans are becoming increasingly popular as a way to boost staff motivation in companies around the world, including the Baltic States. The popularity of stock options is due to how they benefit both the company and the employee. Stock options give employees the right to receive or buy shares in their company after a specified period and for a price below the market value. The company benefits by having employees who are willing to work towards its goals and increase its stock value. Since the national rules for taxing this fringe benefit vary from country to country, it’s important to review the tax laws of Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia.
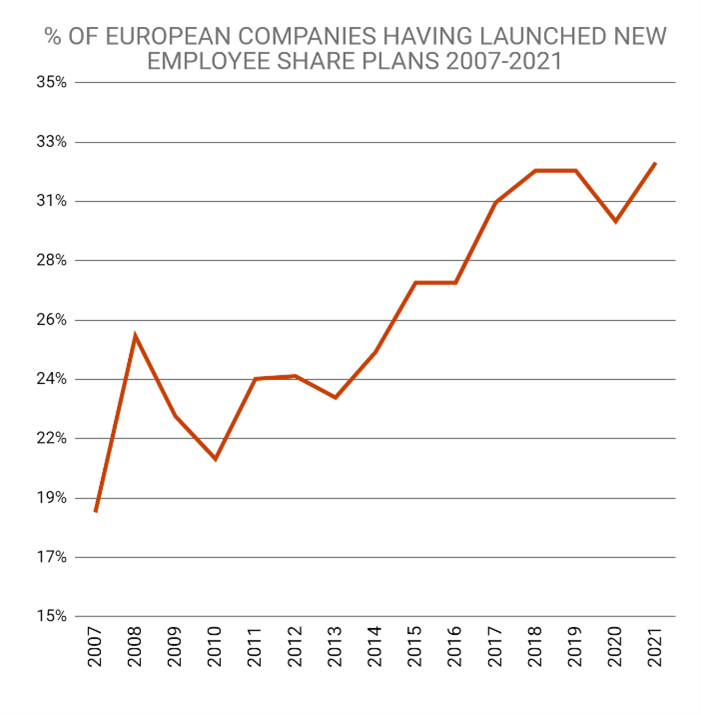
The development of employee stock ownership continues as more and more large European companies are introducing employee stock ownership plans. 32% of the large European companies that took part in our survey1 launched new employee stock ownership plans in 2021, a proportion that tends to grow year on year.
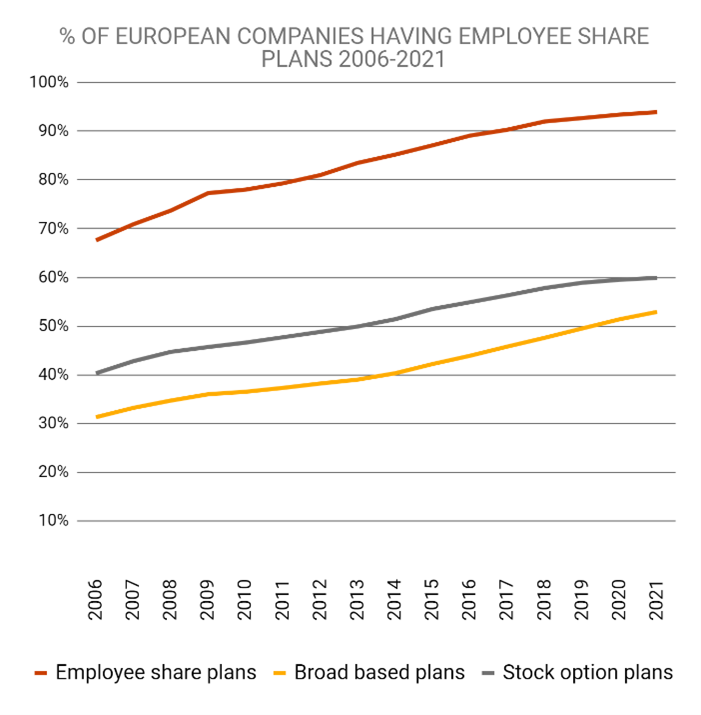
- Employee share plans are fringe benefit plans that give employees an ownership interest in their company in the form of shares (certain, set price).
- Broad based plans mean that most of the company’s full-time employees actually receive stock options over a reasonable period.
- Stock option plans (only for publicly listed companies in our survey) grant stock options for the benefit of employees and the wider public.
PwC’s recent survey examines the tax treatment of equity incentives in startup companies: What’s up for Startups?
The survey focuses on the tax treatment of employee equity compensation plans in startup companies across the EU. The available tax regimes make stock ownership plans way more attractive to startup employees and provide a more startup friendly environment. While these tax regimes expect startup employees to take part in business development, there are many solutions that countries can adopt to pursue that goal.
The purpose of this survey is to provide an overview of the tax treatment of employee equity benefits in startup companies across the EU and some other countries where these types of plans are typically relevant (the UK, Switzerland and Norway).
To encourage employees to achieve goals and complete specific assignments, companies can award or sell stock options (mostly at a zero or discounted price) to its employees. The company and the employee can agree on conditions the employee must meet to acquire such benefits. However, shares can be received after a holding period, which is determined by the company and prescribed by the law.
While the nature of employee stock ownership plans is similar, the conditions for applying the favourable tax treatment are different:
|
Latvia |
Estonia |
Lithuania |
|
|
Taxable unless exemption applies |
When stock options are exercised, tax applies on the difference between the fair market value of shares and the exercise price paid by the employee, if any. |
||
|
Rates |
23% PIT* 34.09% social insurance contributions (SIC) *A progressive 31% PIT applies if SIC are not paid in Latvia. |
20% CIT* 33% SIC *at the rate of 20/80 |
20% PIT SIC consist of the employer part and the employee part. The employee part is withheld at the standard rate of 19.5% (a further 3% must be withheld if the person has joined the Tier 2 pension scheme). The employer part varies from 1.61% to 2.49% and is payable out of the employer’s funds. |
|
Payment and reporting |
The employer must withhold and report PIT to Latvian tax authorities. |
The employer must pay and report CIT and SIC on this fringe benefit to Estonian tax authorities. |
Responsibility to withhold and report PIT to Lithuanian tax authorities: 1) Employer – stock options received from the direct employer 2) Employer – stock options received from a related company Responsibility to withhold and report SIC to Lithuanian tax authorities: 1) Employer – stock options received from the direct employer 2) Employer – stock options received from a related company and the cost of their value recharged to the direct employer (no SIC applicable where the cost is not rechargeable) |
|
Conditions for exemption |
The holding period is at least 12 months. The employee must be in continuous employment during that period. |
An exemption is available if the holding period is at least three years, the employee receives shares in the employer or in a company within the same group as the employer, and the option agreement is signed correctly. |
This may apply to stock options granted by the employer or by a related company after 1 February 2020. No tax applies if the holding period is at least three years. |
All three Baltic countries have introduced a beneficial tax regime to help companies engage their employees in maximising profits. While the conditions for an exemption vary from country to country, it’s easy for employees to receive stock options that are considered tax-free income.
In summary:
1) Stock options are a good long-term motivational tool that is best suited for employees in management positions, as they can directly influence their company’s performance.
2) The relevance of employee stock options is due to the availability of beneficial tax regimes and to the development of local companies.
If you have any comments on this article please email them to lv_mindlink@pwc.com
Ask questionOne of the preconditions for securing positive customer experience is a robust organisational culture. Customer satisfaction is critical to any company seeking to maintain long-term profitability and competitiveness on the market.
Taking care of employees’ mental health is not merely idle chatter or a formal work safety obligation. An employer that fails to pay attention to staff overload issues may face some real legal consequences. This article examines the legal implications of a worker being diagnosed with burnout syndrome and offers a practical overview of how the employer could respond.
We use cookies to make our site work well for you and so we can continually improve it. The cookies that keep the site functioning are always on. We use analytics and marketing cookies to help us understand what content is of most interest and to personalise your user experience.
It’s your choice to accept these or not. You can either click the 'I accept all’ button below or use the switches to choose and save your choices.
For detailed information on how we use cookies and other tracking technologies, please visit our cookies information page.
These cookies are necessary for the website to operate. Our website cannot function without these cookies and they can only be disabled by changing your browser preferences.
These cookies allow us to measure and report on website activity by tracking page visits, visitor locations and how visitors move around the site. The information collected does not directly identify visitors. We drop these cookies and use Adobe to help us analyse the data.
These cookies help us provide you with personalised and relevant services or advertising, and track the effectiveness of our digital marketing activities.